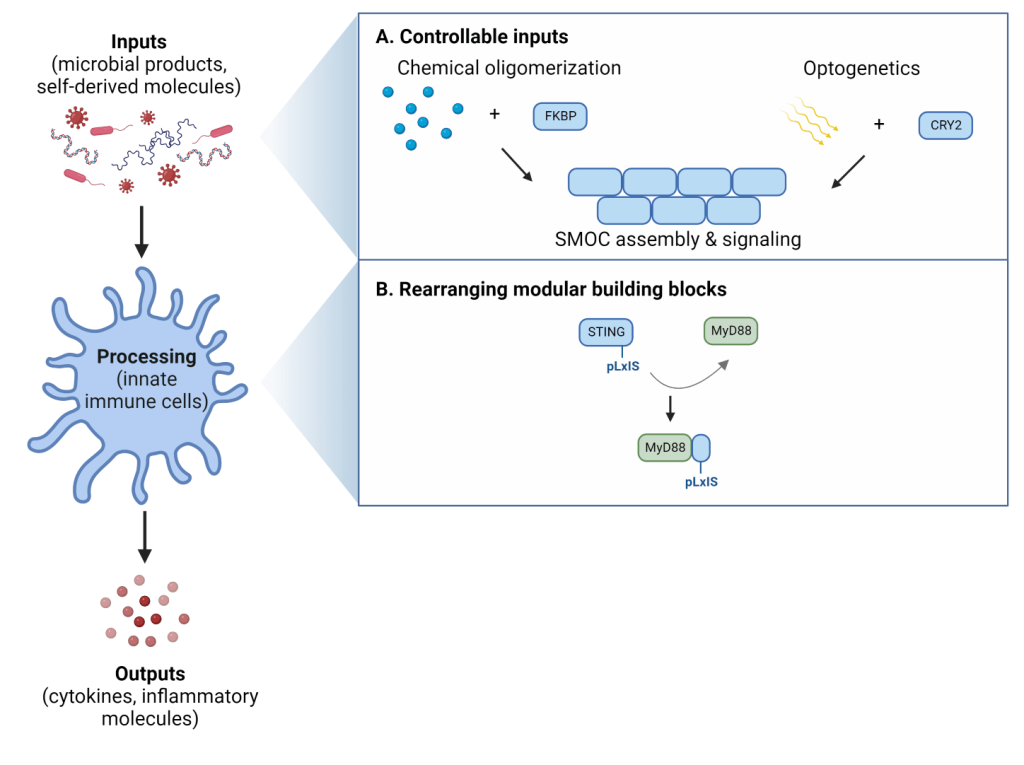
Diverse innate immune cellular responses are transduced through supramolecular organizing centers (SMOCs), which represent the signaling organelles of the innate immune system. The signaling components within SMOCs are modular in nature, such that functional units can be rearranged to rewire downstream outputs. For example, we have engineered myddosomes and inflammasomes to promote interferon activity, and redesigned the LPS receptor caspase-4 to operate as an IL-1β converting enzyme (ICE). Furthermore, we designed synthetic SMOCs that drive chemically-inducible innate immune activities within cells. By exploiting the modular information processing of cells, we can use synthetic biology to engineer new functions and pressure-test biological causality to uncover novel aspects of natural pathway operation.


You must be logged in to post a comment.